Plant IsomiR Atlas (PIA) is a database depositing isomiRs identified from plant landscape.
For this version v1.0, PIA deposits 196,829 unique isomiR
signatures (98,734 unique isomiR sequences) identified from 6,167 plant miRNA hairpins by
using 667 Illumina
small RNA sequencing datasets of 23 species, whose genomes, primary transcripts and
annotation information are mostly from phytozome, except those of Nelumbo nucifera,
which are from lotus-db
(Table 1).
Table 1 Genome backgrounds we used for isomiR identification
| Species |
Source |
Genome |
Transcript |
GO Background |
| Amborella trichopoda |
PhytozomeV11 |
Atrichopoda_291_v1.0.fa.gz |
Atrichopoda_291_v1.0.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Atrichopoda_291_v1.0.annotation_info.txt |
| Arabidopsis lyrata |
PhytozomeV11 |
Alyrata_107_v1.fa.gz |
Alyrata_107_v1.0.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Alyrata_107_v1.0.annotation_info.txt |
| Arabidopsis thaliana |
PhytozomeV11 |
Athaliana_167_TAIR9.fa.gz |
Athaliana_167_TAIR10.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Athaliana_167_TAIR10.annotation_info.txt |
| Brachypodium distachyon |
PhytozomeV10 |
Bdistachyon_283_assembly_v2.0.fa.gz |
Bdistachyon_283_v2.1.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Bdistachyon_283_v2.1.annotation_info.txt |
| Brassica rapa |
PhytozomeV11 |
BrapaFPsc_277_v1.fa.gz |
BrapaFPsc_277_v1.3.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
BrapaFPsc_277_v1.3.annotation_info.txt |
| Carica papaya |
PhytozomeV11 |
Cpapaya_113_r.Dec2008.fa.gz |
Cpapaya_113_ASGPBv0.4.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Cpapaya_113_ASGPBv0.4.annotation_info.txt |
| Citrus clementina |
PhytozomeV11 |
Cclementina_182_v1.fa.gz |
Cclementina_182_v1.0.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Cclementina_182_v1.0.annotation_info.txt |
| Citrus sinensis |
PhytozomeV11 |
Csinensis_154_v1.fa.gz |
Csinensis_154_v1.1.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Csinensis_154_v1.1.annotation_info.txt |
| Glycine max |
PhytozomeV11 |
Gmax_275_v2.0.fa.gz |
Gmax_275_Wm82.a2.v1.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Gmax_275_Wm82.a2.v1.annotation_info.txt |
| Gossypium raimondii |
PhytozomeV11 |
Graimondii_221_v2.0.fa.gz |
Graimondii_221_v2.1.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Graimondii_221_v2.1.annotation_info.txt |
| Malus domestica |
PhytozomeV11 |
Mdomestica_196_v1.0.fa.gz |
Mdomestica_196_v1.0.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Mdomestica_196_v1.0.annotation_info.txt |
| Manihot esculenta |
PhytozomeV11 |
Mesculenta_305_v6.fa.gz |
Mesculenta_305_v6.1.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Mesculenta_305_v6.1.annotation_info.txt |
| Medicago truncatula |
PhytozomeV11 |
Mtruncatula_285_Mt4.0.fa.gz |
Mtruncatula_285_Mt4.0v1.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Mtruncatula_285_Mt4.0v1.annotation_info.txt |
| Nelumbo nucifera |
http://lotus-db.wbgcas.cn/ |
Lotus_mega_gap1M.fa |
lotus_marker_all_mega.gff.CDS |
gene.go.tbl |
| Oryza sativa |
PhytozomeV11 |
Osativa_323_v7.0.fa.gz |
Osativa_323_v7.0.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Osativa_323_v7.0.annotation_info.txt |
| Populus trichocarpa |
PhytozomeV11 |
Ptrichocarpa_210_v3.0.fa.gz |
Ptrichocarpa_210_v3.0.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Ptrichocarpa_210_v3.0.annotation_info.txt |
| Setaria italica |
PhytozomeV11 |
Sitalica_312_v2.fa.gz |
Sitalica_312_v2.2.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Sitalica_312_v2.2.annotation_info.txt |
| Solanum lycopersicum |
PhytozomeV11 |
Slycopersicum_225_iTAGv2.40.fa.gz |
Slycopersicum_225_iTAGv2.3.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Slycopersicum_225_iTAGv2.3.annotation_info.txt |
| Solanum tuberosum |
PhytozomeV11 |
Stuberosum_206_v3.fa.gz |
Stuberosum_206_v3.4.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Stuberosum_206_v3.4.annotation_info.txt |
| Sorghum bicolor |
PhytozomeV11 |
Sbicolor_313_v3.0.fa.gz |
Sbicolor_313_v3.1.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Sbicolor_313_v3.1.annotation_info.txt |
| Triticum aestivum |
PhytozomeV11 |
Taestivum_296_v2.fa.gz |
Taestivum_296_v2.2.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Taestivum_296_v2.2.annotation_info.txt |
| Vitis vinifera |
PhytozomeV11 |
Vvinifera_145_Genoscope.12X.fa.gz |
Vvinifera_145_Genoscope.12X.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Vvinifera_145_Genoscope.12X.annotation_info.txt |
| Zea mays |
PhytozomeV11 |
Zmays_284_AGPv3.fa.gz |
Zmays_284_5b+.transcript_primaryTranscriptOnly.fa.gz |
Zmays_284_5b+.annotation_info.txt |
The species-specific hairpin and mature sequences used for
isomiR identification are from miRBase and
Plant Non-coding RNA Database. We integrated
miRNAs sequences in these two databases and removed the redundancy. Most datasets are from the NCBI
SRA database and transformed into collapsed
FASTA files using in-house Perl script which calls
cutadapt to remove adapter sequences accurately.
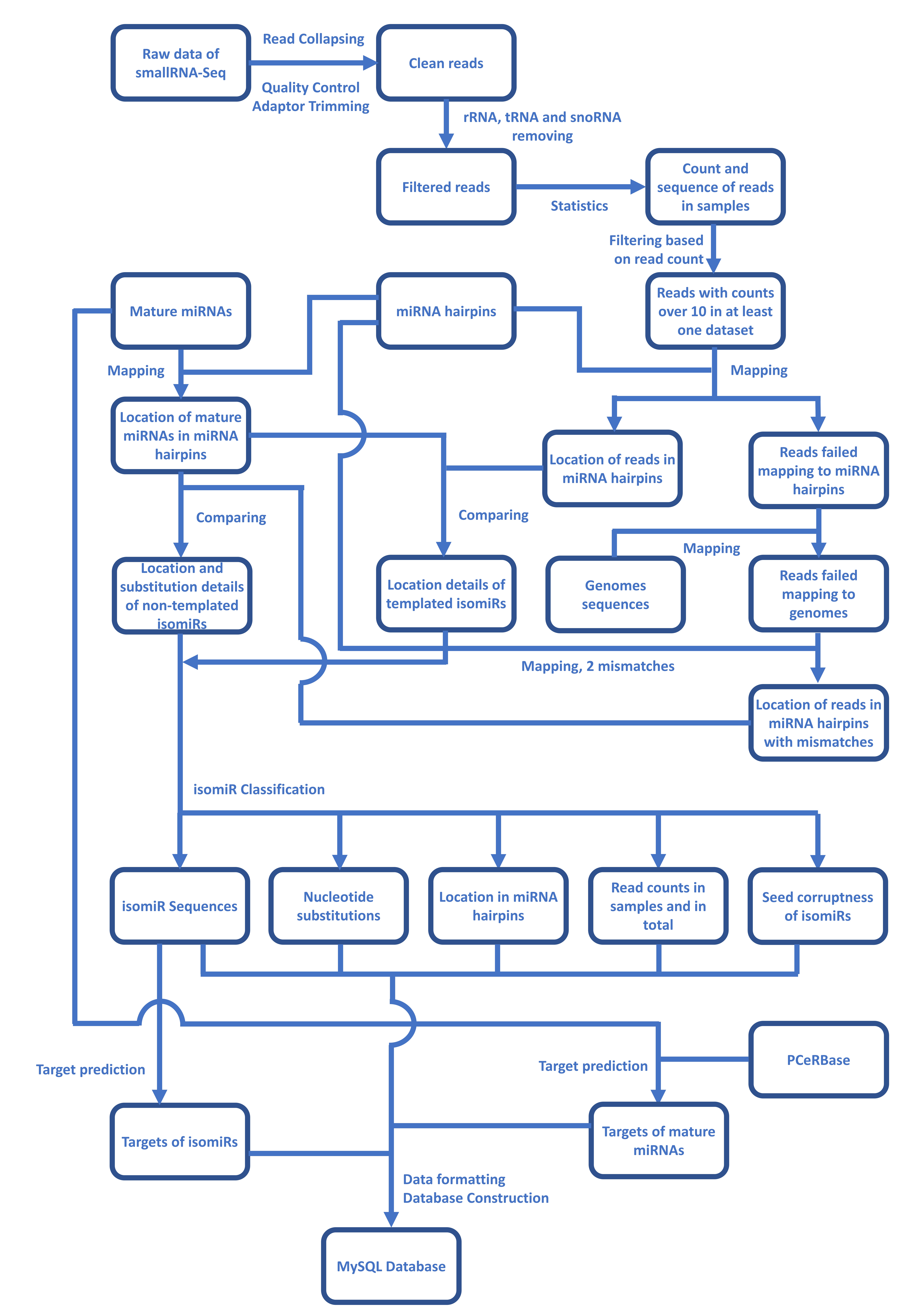
Clean reads are then used for isomiRs identification by a Perl script of modified
isomiR2Function called isomiRIden. Briefly, sequenced reads and canonical miRNAs are
mapped on species-specific pre-miRNAs allowing no mismatch. By comparing mapping information, templated
isomiRs as well as their relative position to canonical miRNAs are identified. After that, reads not mapped on
precursors are mapped on genome allowing no mismatch. Reads not mapped on the genome are then been mapped
on species-specific pre-miRNAs again allowing two mismatches. By comparing mapping information, non-templated
isomiRs as well as their relative position to canonical miRNAs and mismatch positions are identified. Finally, by
analyzing the identified information, isomiRs are indexed and accurately classified into different categories
(Figure 1). You can read our paper "
isomiR2Function: An Integrated Workflow for Identifying MicroRNA Variants in Plants" for more information.